Area characterisation:
Biogeographic region: Humid subtropical and humid continental regimes
Surface area: 360.30 ha
Country: China
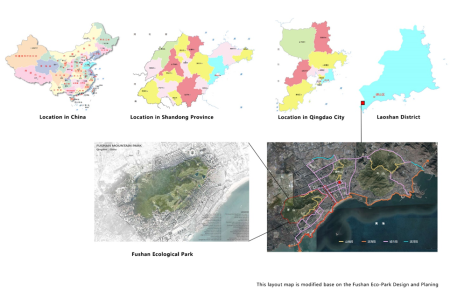
Region/Province: Qingdao, Shandong Province, China (code of Administrative boundary: 370200)
Qingdao is located on China’s Yellow Sea coast. It is a major city in the eastern Shandong Province and has a metropolitan area of 10,654 Km2. It is a major nodal city of the One Belt, One Road initiative that connects Asia with Europe. The permanent resident population in Qingdao is 9.49 million and the urban population has reached 67.92% in 2019. Qingdao is considered as one of the most liveable cities in China, with its fresh sea air, breezy and laidback vibe. With a GDP of 11741.31 billion (2019), Qingdao is also leading Shandong Province in the size of a local economy.
This project is located in Laoshan district, Laoshan is a mountain in Qingdao city near the East China Sea, which is close to the downtown of Qingdao City. The rapid development of urbanisation and tourism of Laoshan district has negative impacts on the city environment and human settlements. The Laoshan has been destroyed by quarrying, and lots of illegal buildings had been built in that mountain. The real estate, hotels and sea farming also destroyed the coastline and habitats of plants and animals. The urban parks are unable to provide enough space for citizens, and the connectivity of urban greenspace landscape is poor.
To restore the Fushan mountain environment in Laoshan districts, the government of Laoshan district has launched this project in 2016. The first goal of this project is to restore the Fushan mountain by NbS and improve the landscape connectivity. And another goal is to provide a space for the recreation of citizens.
Objective:
- Restoring the Fushan mountain through a Nature-Based Solutions approach;
- Improving the landscape connectivity;
- Providing a space for the recreation of citizens.
Actions:
PRINCIPLE UF-NbS (Urban Forests as Nature-Based Solutions) ACTION(S)
Provision of new infrastructure/facilities:
- Restoration of quarry and wastelands, remove the illegal buildings and reforested
- Reforestation and afforestation
- Improvement of landscape connectivity by reconnecting the ecological corridors
- Protect native tree species
- Improvement of water storage and flood management
OTHER PRINCIPLE NbS ACTION(S) – non-UF
- Build new public infrastructures (e.g. roads, toilets, parking lot)
- Recreational and environmental educational activities (e.g., workshops for urban birds, bees or butterfly biodiversity, as well as native tree species, based on the botanic garden and wetlands park)
- Improve the cemetery landscape
- Recover the coastline and beach
- Build the playground for citizens
Lessons learnt:
The whole cycle (including planning and implementation) of Fushan Ecological Park project had been completed in three years (from 2016 to 2018). This project shows the strong administrative capacity has improved the efficiency and effectiveness of the project in a high urbanised area.
Organisations:
1. Governing authorities:
- Zhonghan Sub-district Office in Laoshan District,
- Municipal Public Utilities Bureau in Laoshan District
2. Associations:
- Jinjialing Ecological Protection and Development Center
- Sciences and technology associations (e.g. education and cultural),
- Cultural, and sports, non-government actors (e.g. project contractors, seedling nursery developers, NGO/volunteers, farmers, previous land contractors, scholars and social media)
3. Citizens:
- Park wardens (mostly not volunteer, usually the government pays for them),
- Citizens for maintain and cleaning gardens (not volunteer, e.g. gardeners),
- Citizens who are related association members,
4. Municipalities:
- Zhonghan Sub-district
- Laoshan District
5. Public/private institutions:
- Public institutions:
1) Related departments in Zhonghan sub-district (e.g. budget, communication);
2) Jinjialing Ecological Protection and Development Centre
- State-owned enterprise: Urban and Rural Landscape Planning and Design Institute, China Construction Engineering Design Group Co., Ltd
6. Park planner and authorities:
- Planner: Urban and Rural Landscape Planning and Design Institute, China Construction Engineering Design Group Co., Ltd;
- Authorities and administrative Division: Zhonghan Sub-district Office
7. Technicians for park maintenance/monitoring and to educate and support citizens:
- Zhonghan Sub-district Office and Municipal Public Utilities Bureau in Laoshan District, and other contractors/companies that have contracts with them
Contacts:
Zhonghan Sub-district Office
Qingdao, Shandong Province, China
Tel: + 86 0532-58515625
Global goals:
-
3. Good Health and well being
-
11. Sustainable cities and communities
NBS goals:
- Enhancing sustainable urbanization
- Restoring ecosystems and their functions
- Urban regeneration through nature-based solutions
- Nature-based solutions for improving well-being in urban areas
NBS benefits:
- Increase infiltration / Water storage
- Reducing temperature at meso or micro scale
- Carbon sequestration and storage
- Greater ecological connectivity across urban regenerated sites
- Improve connectivity and functionality of green and blue infrastructures
- Increase Biodiversity
- Increase accessibility to green open spaces
- Increase well-being
- Provision of health benefits
Further information:
The compilation of this case study description has been funded by the Horizon 2020 CLEARING HOUSE project. This project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 821242.