Area characterisation:
Biogeographic region: Coastal
Surface area: 11.968*105 ha
Country: China
Region/Province: Fuzhou/ Fujian
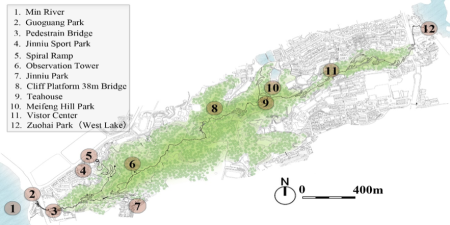
The Fu Forest Trail ('Fudao' in Chinese) is a mountain forest trail project built by the Fuzhou Government since 2016. It is not a traditional ground-based mountain trail, but a new mountainous slow-moving system based on the design concept of a "treetop walkway" (Lowman, 2006; Schwarzer, 2010; Hughes & Morrison-Saunders, 2002). The Fu Forest Trail has a delicate architectural structure, and the trail platform is suspended over a vulnerable urban mountain forest. In August 2018, the Fu Forest Trail was opened to the public. The trail is highly accessible so that at least 200,000 people living in the area can benefit directly (Wang, 2017).
The real purpose of the construction of the Fu Forest Trail is to promote policies related to urban mountains protection and urban green restoration. Actually, as a mountainous city, Fuzhou is facing a dilemma: In the past decade or two, the urbanisation process has swallowed up many of the green hills in the city (Wang, 2017; Yang et al., 2008).
In order to make good use of urban mountains and their associated forest resources, to maintain the characteristics of urban landscape, and to give better consideration to protection and development, the conflicts need to be managed between high-intensity construction requirements brought about by rapid urban development and the conservation of the urban landscape and green open space protection.
Objective:
- Protection of forest coverage and urban greenspace, maintaining the status of urban forests and providing better conditions for forest naturalisation;
- Fostering health and wellbeing benefits gained through the use of the recreation facilities;
- Providing educational facilities for local residents and visitors.
Actions:
PRINCIPLE UF-NbS (Urban Forests as Nature-Based Solutions) ACTION(S)
Provision of new infrastructure/facilities:
- Forest plantations
- Provide a variety of recreational spaces for the public
- Improvement of urban forest landscape connectivity
- Construction of multiple scale urban parks
OTHER PRINCIPLE NbS ACTION(S) – non-UF
- Recycling of construction waste/garbage (e.g. using concrete from removed buildings in landscape architecture such as park paths, garden ornaments)
- Recreational and environmental educational activities (e.g., workshops for urban birds, bees or butterfly biodiversity)
Lessons learnt:
The design of the Fu Forest Trail adopts many new concepts that are different from the traditional urban forest trails, creating a precedent for the rigid frame suspended plank road in China. It has aroused great interest of the public, made the Fu Forest Trail famous abroad, and exerted a huge social impact. Although the treetops have a wide view and good air permeability, the shading effect is slightly worse; We hope that Fu Forest Trail can provide reference and help for the designing of similar projects.
Organisations:
1. Governing authorities: Fuzhou Greening Office, Fuzhou Gardening and Greening Bureau, Metropolitan City of Fuzhou
2. Associations: Sciences and technology associations (e.g. education and cultural), cultural, and sports, non-government actors (e.g. project contractors, seedling nursery developers, NGO/volunteers, previous land contractors, scholars and social media)
3. Citizens: Park wardens (mostly non-volunteer, usually the government pays for them), citizens for maintain and cleaning gardens (non-volunteer, e.g. gardeners), citizens who are related association members
4. Municipalities: Municipalities of Gulou Districts
5. Public/private institutions: Public institutions: Office of Planning and Development, Office of Voluntary Tree Planting (under the framework of Capital Greening Office); Municipalities of local districts (e.g. District Gardening and Greening Bureaus); Research institutes or universities that have be involved in this project (e.g. Fuzhou Forestry University, Research Institute of Forestry Chinese Academy of Forestry); no private institutions since this project was mainly funded by municipal and district government revenues
6. Park planner and authorities: Planner: Look Architects (Singapore); Authorities and administrative Division: Fuzhou Gardening and Greening Bureau
7. Technicians for park maintenance/monitoring and to educate and support citizens: Office of Park Management (technicians, administrative personnel, and workers); Environmental Education Department
Contacts:
Fuzhou Municipal Forestry and Parks Bureau, Fudao Park Service Center
Fuzhou, China
Tel: + 86 (0591) 83768730
WeChat:FuForestTrail
Global goals:
-
3. Good Health and well being
NBS goals:
- Enhancing sustainable urbanization
- Urban regeneration through nature-based solutions
- Nature-based solutions for improving well-being in urban areas
NBS benefits:
- Increase well-being
Further information:
The compilation of this case study description has been funded by the Horizon 2020 CLEARING HOUSE project. This project has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 821242.