Resource description:
Methodology for assessing direct and indirect flood based economic losses to allow prioritisation and evaluation of adaptation measures.
Author/Contact:
TURAS
Expert contact: Elco Koks
Advantages:
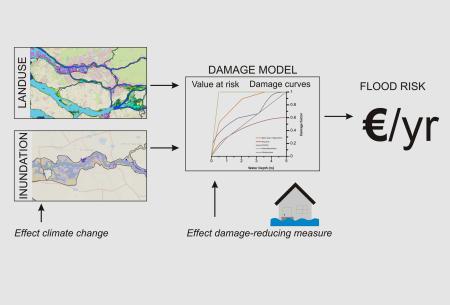
- In order to support decision making in flood risk management, it is necessary to have reliable estimates of the potential consequences. Integrated modelling of direct damage and indirect losses, linked to specific flood events (i.e. 1/100 year flood) is n
- This methodology requires: 1) The collection of relevant data related to the hydrological system and/or flood events; 2) The collection of relevant information on exposure (i.e. land-use assets); 3) The collection of economic data (e.g. input-output ta
Constraints:
- Floods constitute a major natural hazard, resulting in large global losses every year. This relates to both the direct damage caused by flooding (i.e. to buildings, crops) as well as the economic-wide impact that can go beyond the flooded area itself, and
Uses of this resource:
On the one hand, with climatic change affecting the global, regional and local water systems (i.e. in the form of sea-level rise), the risk of flooding and flood hazards is increasing. On the other hand, global population continues to grow, and with increased urbanisation, modern cities are becoming more and more dense in terms of people and valuable assets. They can be characterised as high-risk damage intensive areas, where a high level of connectivity can lead to spatial and temporal chain reactions.
Additional information:
WHO SHOULD BE INVOLVED?
FACILITATORY (PUBLIC) BODIES:
land use planning department; planning and development department; water and sewerage management department; environmental and sustainability department; socio-economic development department
LOCAL TASK FORCE:
local or regional authority; professional expert
SUITABLE FOR:
dense inner city; urban region; (sub-)urban communities
MAIN NECESSARY RESOURCES ARE:
monetary investments; expert knowledge; public institutional set-up; local knowledge
Licence:
- Free, no licence
Development stage:
- Full, working product