Resource description:
Methodology for detailed urban heating demands and related energy consumption.
Author/Contact:
TURAS
Expert contact: Steffen Nielsen
Advantages:
- The solution is to transition fossil-fuel energy supply systems into renewable energy systems. This is not a simple task, as a change towards renewable energy requires improvements of the whole energy supply system, the development of new technologies as
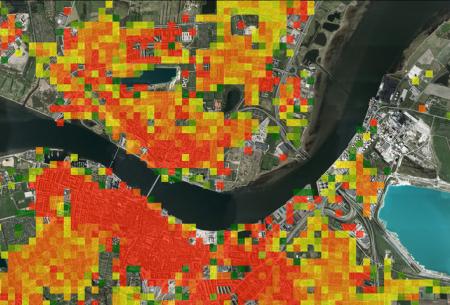
- In this sense, the "Urban Heat Atlas" is a tool that helps this transition by assessing current heat demands, potentials for reductions as well as potentials for district heating through the use of technologies that enable an efficient use of renewable en
- An "Urban Heat Atlas" is a geographic database that includes estimated heat demands of single building units. Typically, heat demands are estimated based on building characteristics such as age, type, use, and size. However, this is very dependent on what
Constraints:
- A significant share of the present energy consumption is related to building heating systems as well as the supply of domestic hot water. As current heat supply systems are mainly based on fossil fuels, the energy consumption in buildings ultimately contr
Uses of this resource:
The problem with energy use in buildings exists because development so far has primarily been based on the utilization of fossil fuels such as oil, gas, and coal. With more than 80% of the world’s primary energy consumption based on fossil fuels and rapid population growth rates, their use is significantly increasing. This not only contributes to increase natural resource depletion but also produces a variety of environmental impacts. For instance, fossil fuel combustion releases greenhouse gases that contribute to global warming, which has a negative impact on weather, oceans, food supply, health, and biological systems.
Additional information:
WHO SHOULD BE INVOLVED?
FACILITATORY (PUBLIC) BODIES:
planning and development department; environmental and sustainability department; energy and waste department; architecture department
LOCAL TASK FORCE:
professional expert; researcher; business
SUITABLE FOR:
dense inner city; urban region; (sub-)urban communities; underused urban site & building
MAIN NECESSARY RESOURCES ARE
monetary investments; expert knowledge; local knowledge
Licence:
- Free, no licence
Development stage:
- Full, working product