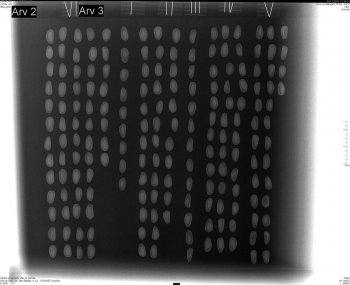
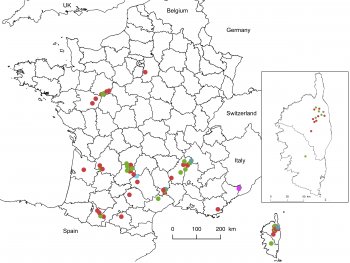
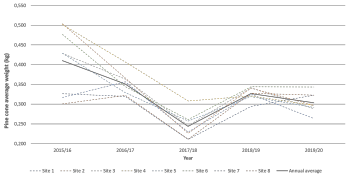
Pine cone quality assessment with X-Ray
The objective is to analyze the possibility of modeling the kernel weight from biometric and morphological parameters of the pine nuts from Pinus pinea, measured through X – ray and image analysis. The overall objective is to support the definition of a pine cone quality assessment methodology at the stand/ farm level in order to provide the landowners with tools for pine cone commercialization and increase by this mean the market transparency.