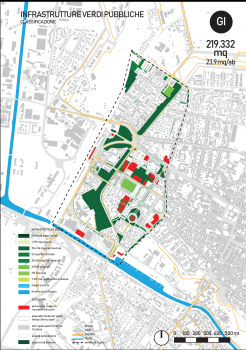
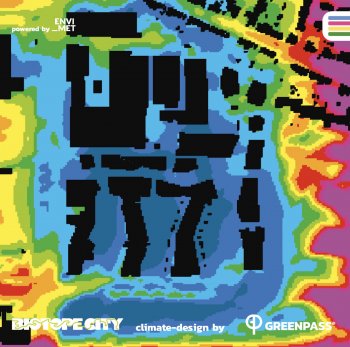
The Portable Modular Natural Biological System, PM-NBSTM developed by AYALA WATER & ECOLOGY
To improve and validate a portable, modular, enery-free, decentralized water treatment system, the PM-NBSTM, to remediate source water to high quality for resuse, filling a major gap in small agglomerations and remote areas where good quality waters are needed and no other solution is feasible