Tunisian Salvia officinalis essential oils: Variations regarding plant organs, harvest season and drying conditions
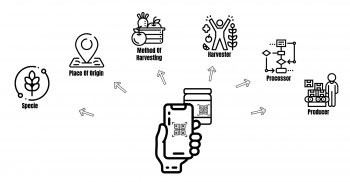
This study presents an assessment of essential oils amounts and quality obtained from Tunisian Salvia officinalis and its variations regarding the plant organs, the harvest season and the plant's drying process conditions. Three drying processes were tested, natural air drying, hot air convective drying at two temperature 40 and 60°C and microwave drying at 218 W.