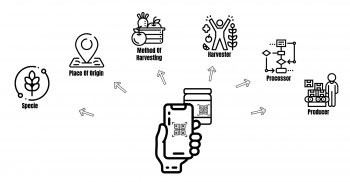
A comprehensive training program for AMP exploitation
During the last years there has been a growing interest from young people to get involved in the AMP exploitation business. The rich Greek flora and the plenty of abandoned agricultural fields in rural areas offer a great potential in this direction. However, most of the young farmers/entrepreneurs didn’t have a relative experience in the field and there has been many fails and disappointments.