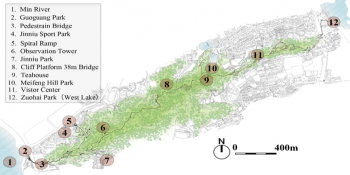
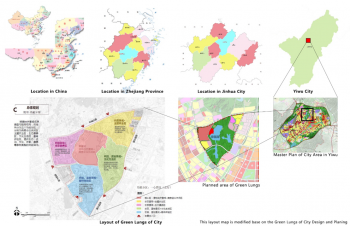
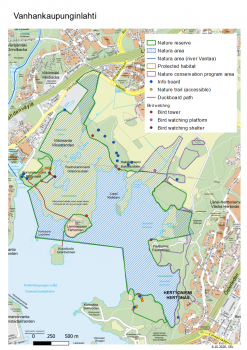
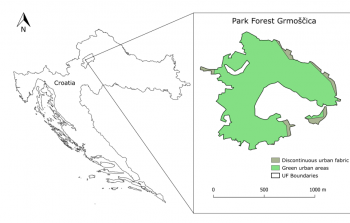
Water Haigh Woodland Park, Lower River Aire Valley – Leeds, UK
The case study site provides connected multi-functional green space that maximises ecosystem services for the sites and the local communities. Objectives include:
- The provision of regionally important landscape scale natural habitats, encompassing mixed woodlands, hedgerows, grasslands and wetlands, encompassing the reclamation of UF-NbS (Urban Forests as Nature-Based Solutions) of previously mined industrial land.
- The provision of unlimited public access via footpaths, cycle ways and bridle ways;
- The health and well- ...