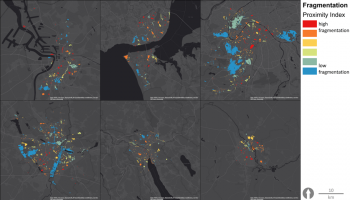
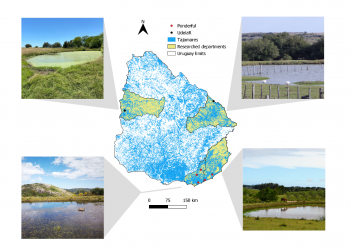
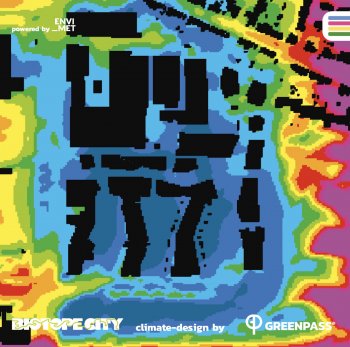
Managing urban Biodiversity and Green Infrastructure to increase city resilience in Ghent (UrbanGaia project)
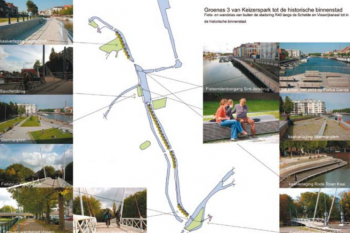
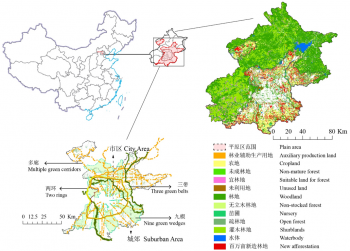
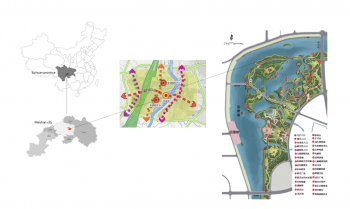
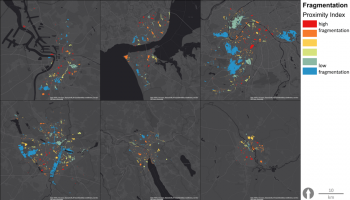
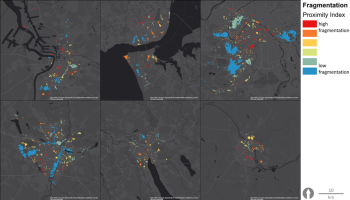
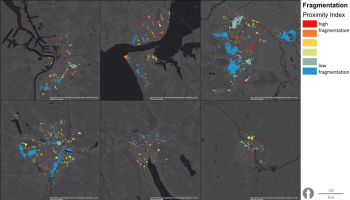
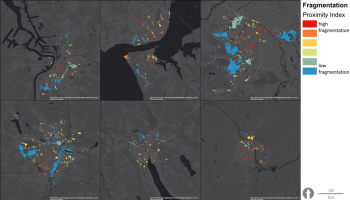
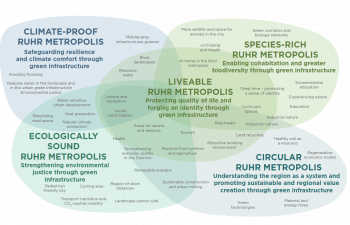
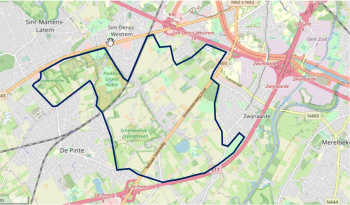
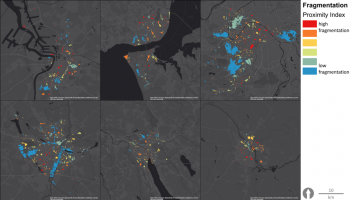
The aim is to develop a realistic framework of indicators to evaluate, manage and develop performant Urban Green-Blue Infrastructure (U-GBI) in cities and intensively managed landscapes. UrbanGaia explicitly focusses on analysis of ecological and socio-economic features of the many existing GBIs. The evaluation of one the green axis of the ecological network in Ghent will serve as a case study for the framework of indicators. Furthermore, policy, governance and management practices of U-GBI are analyzed to identify innovative approaches to GBI implementation and usage.